
Dr. Simit Vora
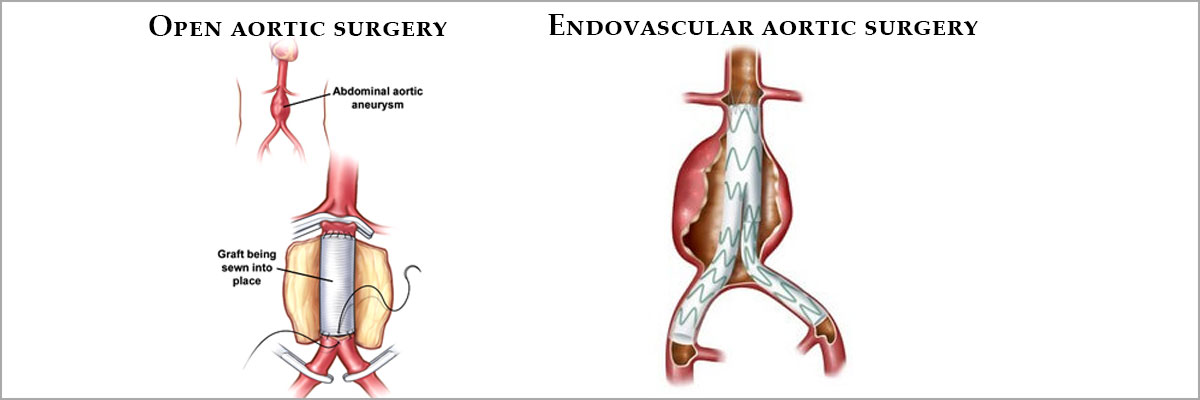
Open aortic surgery
Open aortic surgery (OAS), also known as open aortic repair (OAR), describes a technique whereby an abdominal, thoracic or retroperitoneal surgical incision is used to visualize and control the aorta for purposes of treatment, usually by the replacement of the affected segment with a prosthetic graft. OAS is used to treat aneurysms of the abdominal and thoracic aorta, aortic dissection, acute aortic syndrome, and aortic ruptures. Aortobifemoral bypass is also used to treat atherosclerotic disease of the abdominal aorta below the level of the renal arteries. Dr Simit Vora is Doctor for Deep Vein Thrombosis Treatment in Borivali
Depending on the extent of the aorta repaired, an open aortic operation may be called an Infrarenal aortic repair, a Thoracic aortic repair, or a Thoracoabdominal aortic repair. A thoracoabdominal aortic repair is a more extensive operation than either an isolated infrarenal or thoracic aortic repair. Dr Simit Vora is Doctor for Deep Vein Thrombosis Treatment in Borivali
OAS is distinct from aortic valve repair and aortic valve replacement, as OAS describes surgery of the aorta, rather than of the heart valves. When the aortic valve is diseased in addition to the ascending aorta, the Bentall procedure is used to treat the entire aortic root. An axillary-bifemoral bypass is another type of vascular bypass used to treat aortic pathology, however it is not true open aortic surgery as it reconstructs the flow of blood to the legs from the arm, rather than in the native location of the aorta.
Medical uses
OAS is used to treat patients with aortic aneurysms greater than 5.5 cm in diameter, to treat aortic rupture of an aneurysm any size, to treat aortic dissections, and to treat acute aortic syndrome. It is used to treat infrarenal aneurysms, as well as juxta- and pararenal aneurysm, thoracic and thoracoabdominal aneurysms, and also non-aneurysmal aortic pathology. Disease of the aorta proximal to the left subclavian artery in the chest lies within the specialty of cardiac surgery, and is treated via procedures such as the valve-sparing aortic root replacement. Prior to the advent of EVAR, OAS was the only surgical treatment available for aortic aneurysms. It is still preferred at some institutions and by some patients as it may be more durable than EVAR and does not require post-operative surveillance CT scans. OAS is sometimes required for patients who have previously undergone EVAR but need further treatment, such as for degeneration of the EVAR seal zones leading to continued aneurysm growth. OAS is also sometimes required in cases of EVAR graft infection where the stent graft is removed to treat the infection
Open Repair versus Endovascular Repair
The shift away from open aortic surgery towards endovascular surgery since 2003 has been driven by worse perioperative mortality associated with OAS, particularly in patients in relatively frail health. Unlike endovascular repair, there are no strict anatomic contra-indications to open repair; Rather, open repair is viewed as the fall back option for patients with unfavorable anatomy for endovascular repair. The main drawback of open repair is the larger physiologic demand of the operation, which is associated with increased rates of short term mortality in most studies Patients younger than 50 years with descending and thoracoabdominal aortic aneurysm have low surgical risks, and open repairs can be performed with excellent short-term and durable long-term results. Open surgical repairs should be considered initially in younger patients requiring descending and thoracoabdominal aortic aneurysm repairs. Heritable thoracic aortic disease (HTAD) warrants closer postoperative surveillance
Endovascular Aneurysm Repair
An aortic aneurysm is a bulging, dilation or ballooning in the wall of a blood vessel, usually an artery, that is due to weakness or degeneration that develops in a portion of the artery wall. Just like a balloon, the aneurysm enlarges, stretching the walls of the artery thinner which compromises the artery wall's ability to stretch any further. At this point, an aneurysm is at risk of rupturing and causing potentially fatal bleeding, just as a balloon will pop when blown up too much. Dr Simit Vora is Doctor for Deep Vein Thrombosis Treatment in Borivali
UCSF has a world-renowned program in endovascular surgery, one of the largest and oldest in existence. Vascular surgeons at UCSF have extensive experience in performing technically challenging surgeries for complex aortic aneurysms, such as those involving arteries running to the kidneys and intestines, and have pioneered many endovascular procedures for treating aneurysms in use today.
What is endovascular aneurysm repair?
Endovascular aneurysm repair involves inserting a graft within the aneurysm through small groin incisions using X-rays to guide the graft into place.
The advantage of this type of repair is that there is no abdominal surgery. This technique is therefore safer than the traditional operation, and you need to spend less time in hospital. A disadvantage is that some patients have to undergo a further operation at a later stage to refine the initial procedure.
Not every patient or every aneurysm is suitable for EVAR. In particular, aneurysms arising close to or above the kidneys are more difficult to treat in this way. You will be assessed with a scan to determine if your aneurysm can be treated by endovascular repair. If suitable you will be offered a choice of type of repair by your surgeon. If this cannot be undertaken at your local hospital, you may need to travel to a centre that can perform endovascular repair. Dr Simit Vora is Doctor for Deep Vein Thrombosis Treatment in Borivali
